Offshore Wind Power
Harnessing Abundant Offshore Wind Resources — A Leading Force in Next-Generation Clean Energy
Japan Wind Development aims to revitalize coastal regions through its offshore wind power business, leveraging the expertise and knowledge it has accumulated over the years.
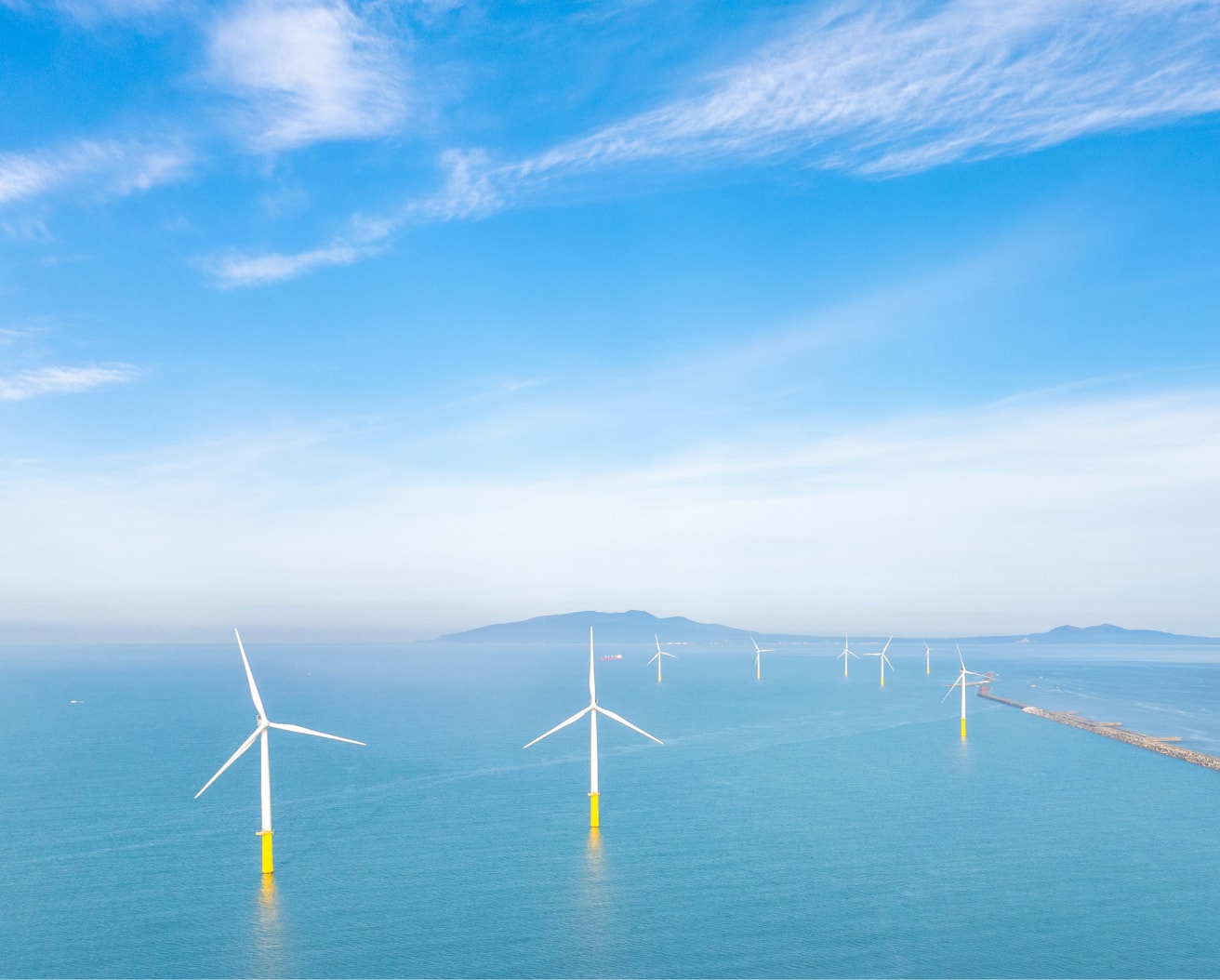

What is Offshore Wind Power Generation?
Offshore wind power, which involves installing wind turbines at sea, is a promising next-generation clean energy source. Compared to land, offshore areas offer stable wind conditions with fewer geographical obstructions like mountains, making them ideal for wind energy production. As global adoption increases, technologies related to offshore wind construction and operations are rapidly advancing. In Japan, offshore wind is expected to play a leading role in the country’s clean energy future.
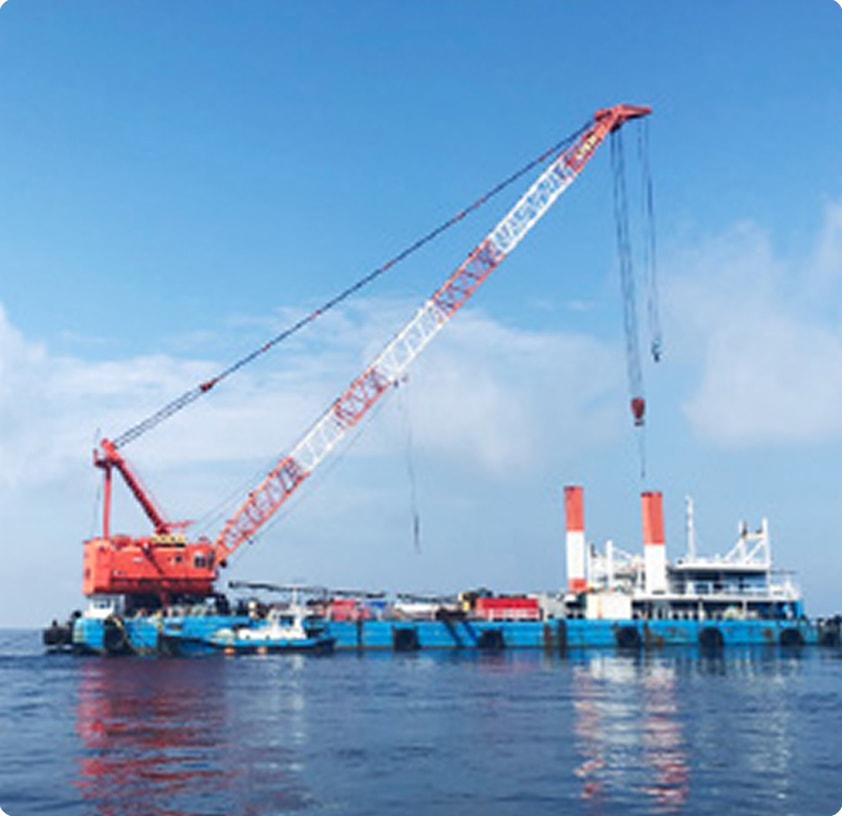
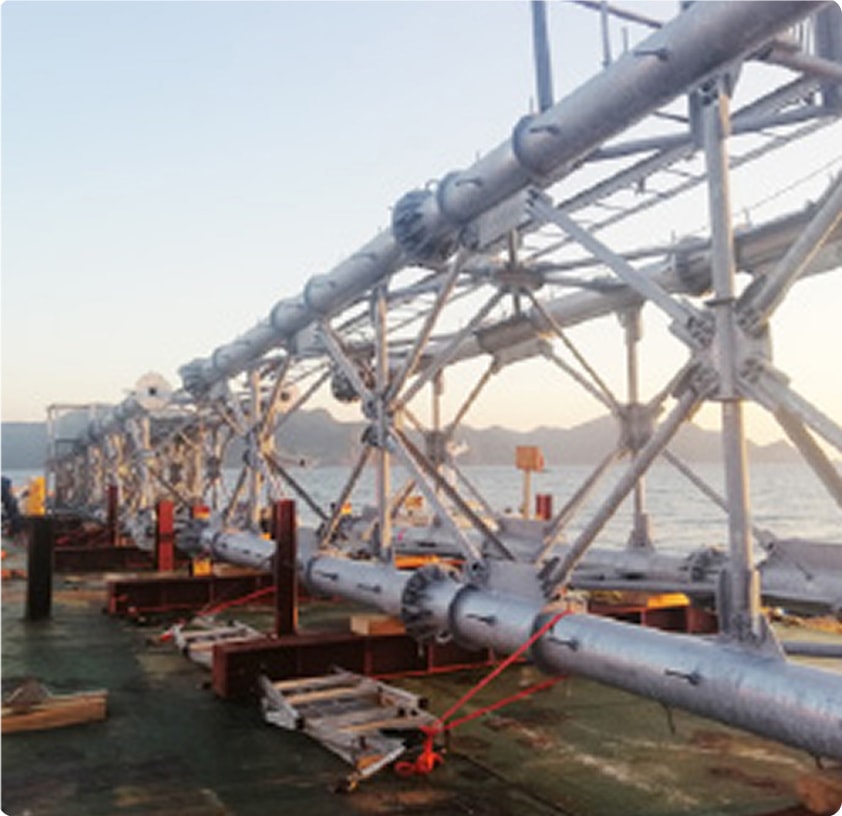
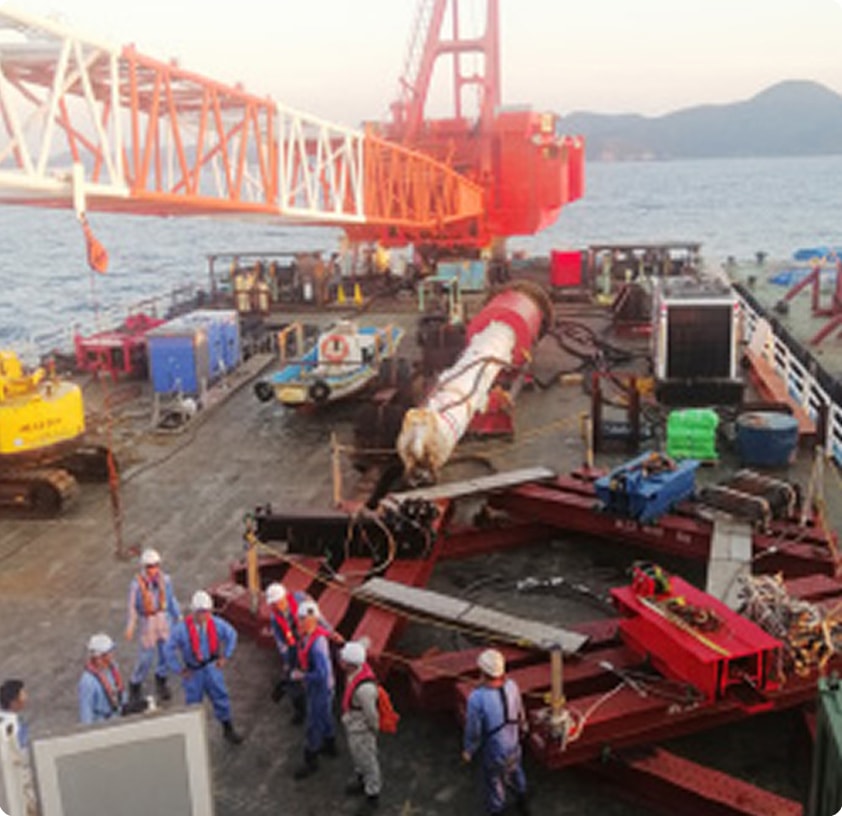



Anticipated Economic Benefits, Including the Creation of New Industries
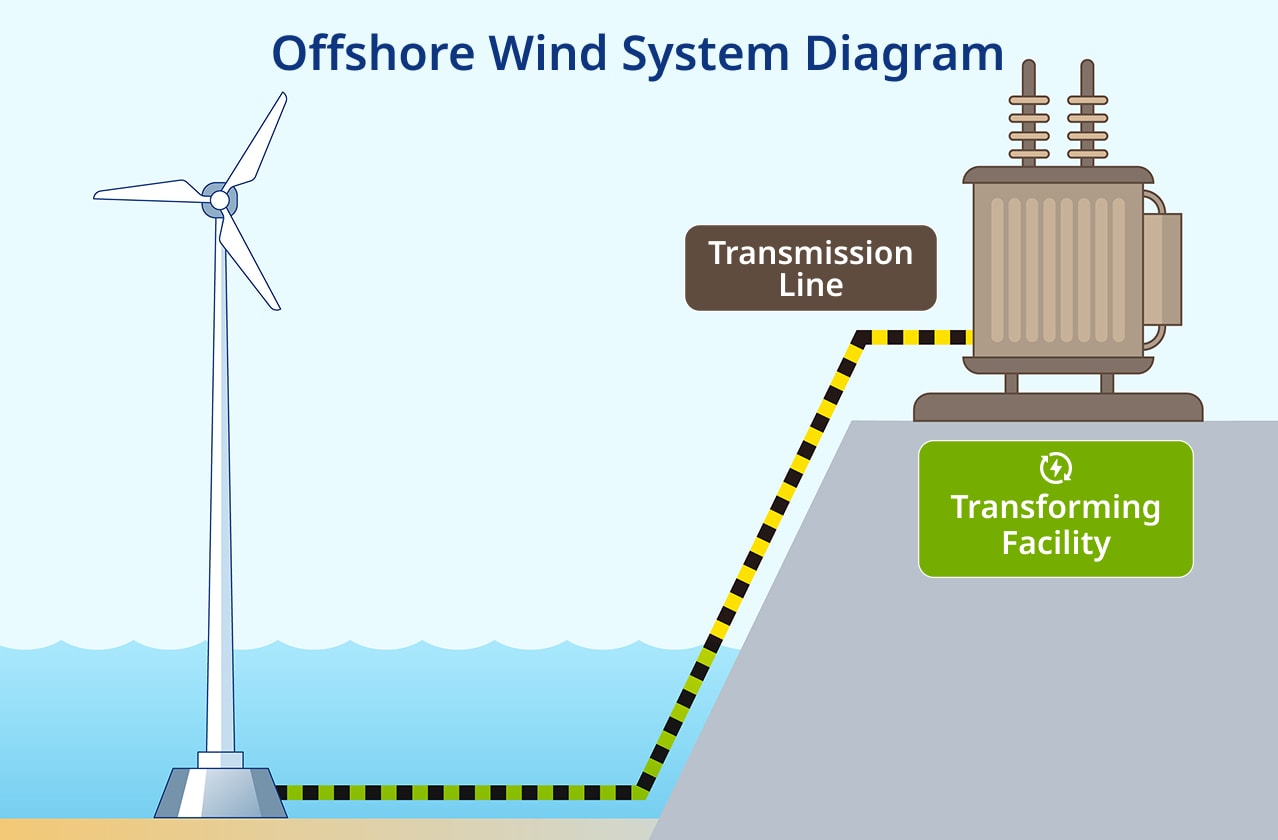
Offshore wind farms typically consist of turbines, foundations, offshore substations, and subsea cables that connect them to the land-based grid. The ocean's vast space enables the installation of large-scale wind farms. With turbines becoming larger, further improvements in efficiency are anticipated.
Trend Toward Larger Turbines and Higher Output
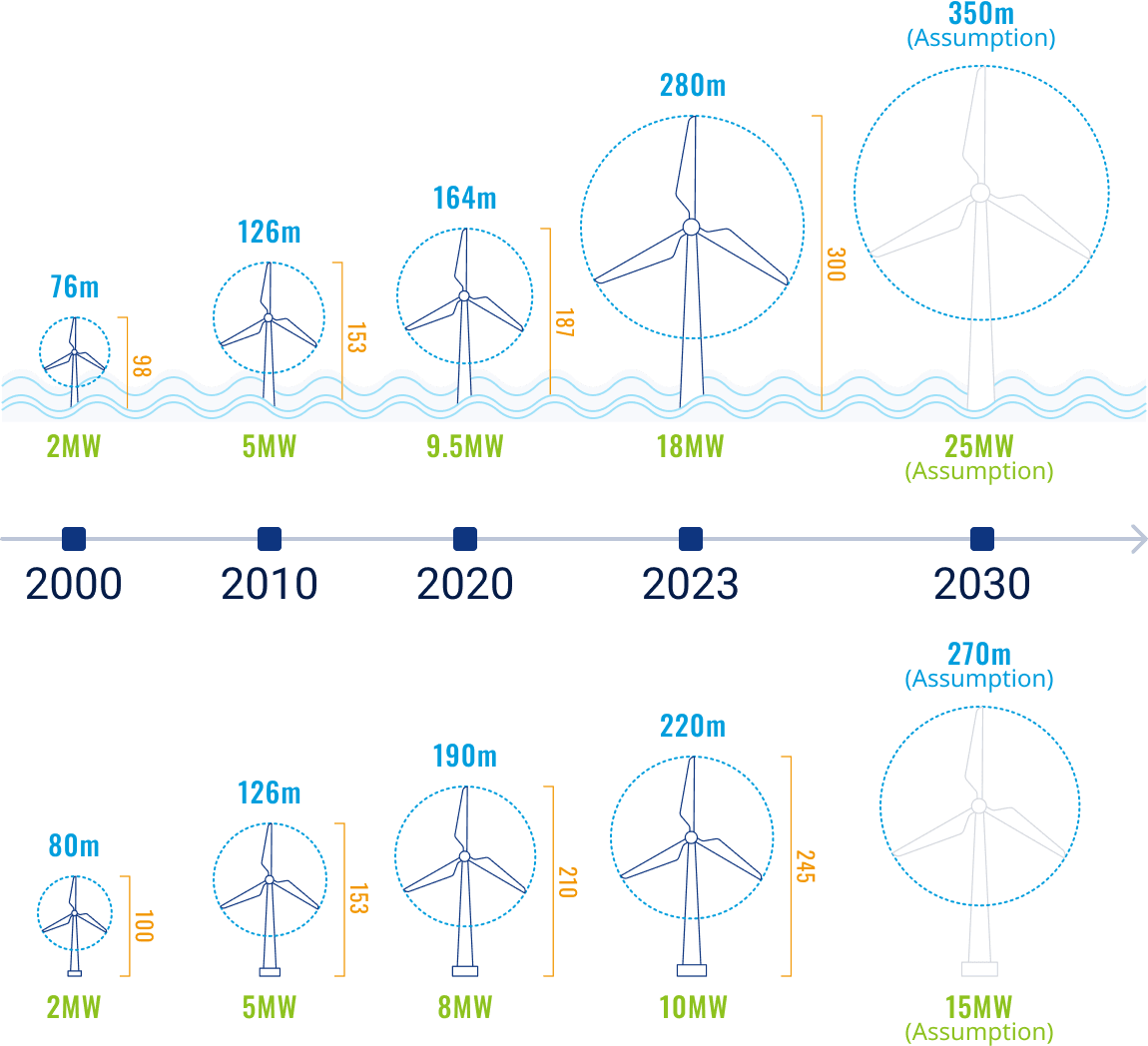
Source:GWEC Market Inteligence
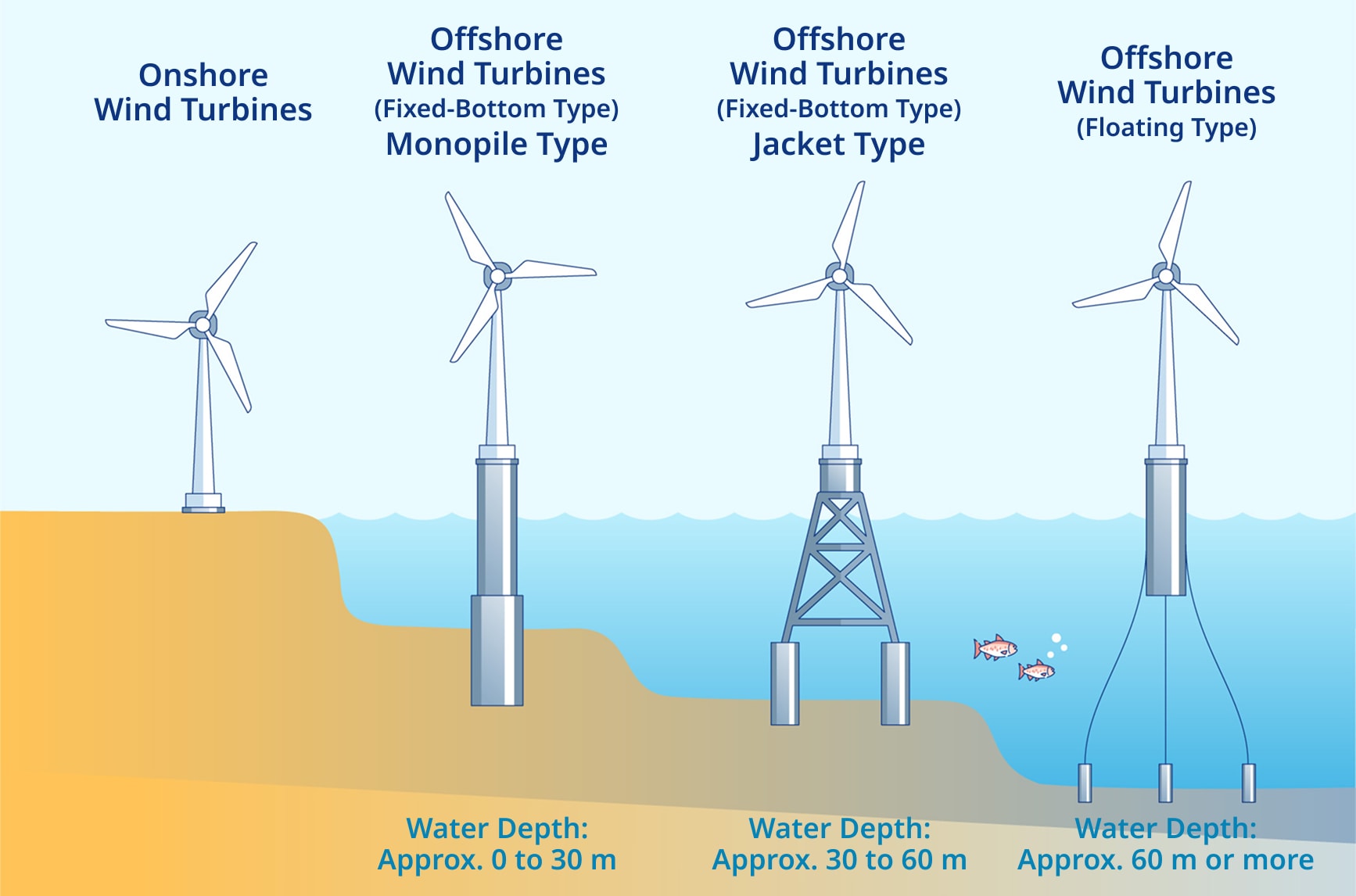
Installation Methods
There are two main types of offshore wind turbine foundations:
Fixed-bottom (Monopile or Jacket): These are anchored to the seabed and are suitable for shallow waters. They offer stability and can accommodate large turbines.
Floating: These turbines are installed on floating platforms and can be deployed in deeper waters, expanding site possibilities.
Growing Expectations for Offshore Wind Power
Driven by increased electricity demand due to the expansion of data centers, the implementation of AI, and broader digitalization, along with the global shift toward decarbonization, offshore wind power—a renewable energy source—is gaining increasing attention. Japan, being surrounded by the sea, possesses geographic characteristics highly suitable for offshore wind development. To improve the nation’s energy self-sufficiency and achieve carbon neutrality, the acceleration of offshore wind power deployment is essential.
Domestic and International Deployment Status
Globally, installed offshore wind capacity has grown significantly, from 3.8 GW in 2011 to 63.2 GW in 2022, with Europe and China leading the way.
In contrast, Japan’s installed capacity stood at only 58.6 MW as of 2020. The Japanese government has set ambitious targets, to install 10 GW by 2030 and 30–45 GW by 2040.

Position in the 7th Strategic Energy Plan
In Japan’s 7th Strategic Energy Plan, offshore wind is identified as a power source with strong potential for cost reduction in the future. It is expected to play a meaningful role in the country’s energy mix. Reflecting rapid cost declines and project development abroad, offshore wind has been positioned domestically as a key driver in making renewables a mainstay energy source.

Our Company’s Efforts and Strengths
Our company has established strengths in project development, construction, and O&M, allowing us to manage the entire upstream to midstream value chain seamlessly. With extensive experience since the early days of wind power in Japan, we are committed to applying the expertise gained from onshore wind to continue advancing into the offshore wind sector.

